Every user can browse data online via a taxonomic tree (“Browse taxa”), view the data completeness (“Data completeness”), and download the entire database or specified subsets in several formats (see “Download data”). Registered users – i.e. those who want to contribute trait information to the Black Sea Traits Database – have additional options summarized below (“Database manual for registered users”).
Database manual for registered users
- 1. Login
- 2. Getting started
- 3. Adding taxa to the database
- 4. Dataset management
- 5. Adding trait and source information
- 6. References
1. Login
Once a user entry is received from the editor, the restricted area of the database can be accessed via the "Login" button on the public page (Fig. 1).

2. Getting started
2.1. The top menu bar
After signing in the user is transferred to a starting page with a top menu bar of seven headers (Fig. 2, Table 1). In addition, an alphabetic list of all taxa in the database is displayed (grouped in species/genus/family level taxa). The taxon list can be filtered for datasets (see Sect. 4) or phyla. Each taxon name links directly to the respective taxon page (see Sect. 5).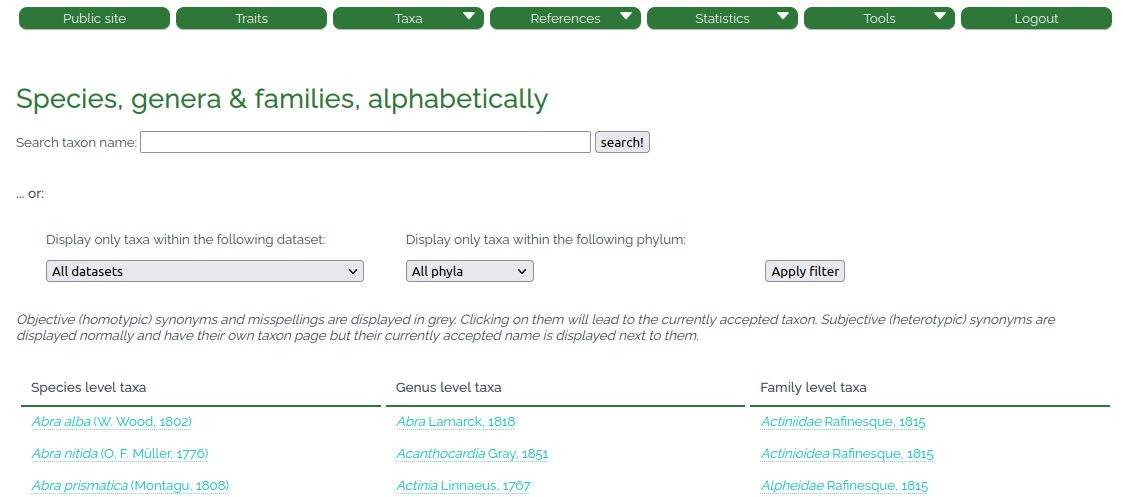
| Header | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Public site | Transfer back to the public page. | ||
| Traits | Show a list of the traits included in the database. Each trait links to all those taxa for which information on this specific trait exists. | ||
| Taxa | Taxa alphabetically | Alphabetic list of taxa, same than starting page. | |
| Classification | Classification tree, branches can be expanded by mouse click and taxa can be selected. | ||
| Add new taxon | Manual entry of taxa | Sect. 3.1 | |
| Aphia batch entry | Batch entry of up to 50 taxa via their Aphia IDs | Sect. 3.2 | |
| References | List of references | Show full list of included sources. | Sect. 6 |
| Add new reference | Entry window for new reference or observation | Sect. 5 | |
| Statistics | My data | Overview of all entries made by the respective user. | |
| Tools | Dataset management | Add a new dataset. | Sect. 4 |
| Remove an existing dataset. | Sect. 4 | ||
| Add taxa to an existing dataset. | Sect. 4 | ||
| Remove taxa from an existing dataset. | Sect. 4 | ||
| Data with conflicts | List all taxa for which conflicts are detected. | Sect. 5 | |
| Logout | Log the user out of the system and take them back to the public site (Fig. 1). | ||
3. Adding taxa to the database
As trait information is always connected to specific taxa, as a first step, the respective taxon ( Sect. 3.1) or a whole list of taxa (Sect. 3.2) has to be entered or uploaded. Optionally, the taxa can be organized into specific datasets, e.g. linking to a specific sampling campaign and location (see Sect. 4).
3.1. Manual entry of taxa
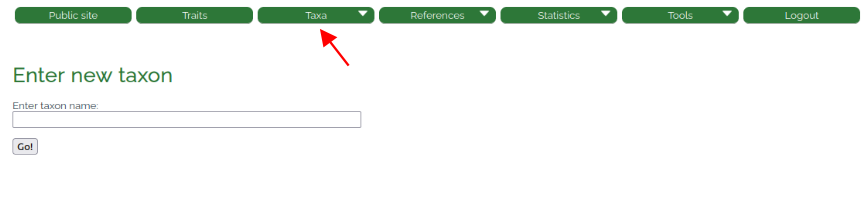
The system allows data entry at different taxonomic levels, from species to phylum. Via the "Taxa" dropdown in the top menu and "Add new taxon" (Fig. 3, Table 1) taxon names can be entered one by one manually. In that case, the system will query the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS Editorial Board, 2021) for the taxon, may correct for misspellings, and will then enter the taxon and its higher classification automatically. In the event that taxon names have changed ("unaccepted" in WoRMS), we recommend to stick to the original taxon name as information might end up attached to the wrong taxon if the classification changes again at any point in the future. In the database, synonyms are displayed and deep-linked to WoRMS in the taxonomic tree on the taxon page. If the taxon is already included in the database, a message is displayed and the taxon is not entered, thus avoiding duplicates. The user can of course still add trait information to the already existing taxon (Fig.5).
3.2. AphiaID batch entry
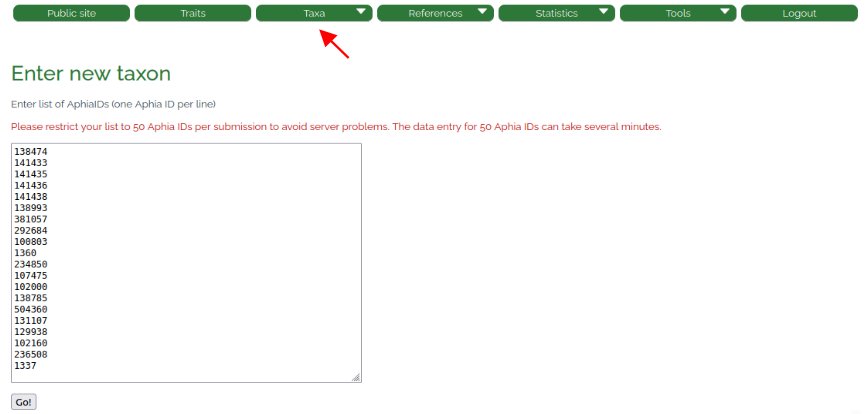
Adding of multiple taxa at once is possible via the "AphiaID batch entry" function in the "Taxa" dropdown menu (Fig. 4). This function allows to enter up to 50 AphiaIDs at the same time. The system will query WoRMS for the taxa for these AphiaIDs, and enter them automatically. In this case, the taxon names first need to be matched to WoRMS by the user (see taxon match tutorial at the World Register of Marine Species ). In the event that AphiaIDs have changed ("unaccepted" taxa in WoRMS), we recommend to stick to the original AphiaID ( Sect. 3.1). Again, if a taxon is already included in the database, a message is displayed and the taxon is not entered.
4. Dataset management
In the "Tools" section, taxa can be allocated to one or more specific datasets via the "dataset management" function. This can be done either to organize a user’s working process, to ensure a certain degree of traceability to the original data source and to the region where the taxon was sampled, or to be able to export only pre-defined subsets of data. A taxon can be linked to any number of datasets. In case the connection of a taxon to a specific dataset is no longer desired, it can – again via the "dataset management" function – easily be removed from the dataset ("Remove taxa from an existing dataset"), or added to another ("Add taxa to an existing dataset"). In any case, the taxon or the trait information tied to this taxon is thereby not affected.
5. Adding trait and source information
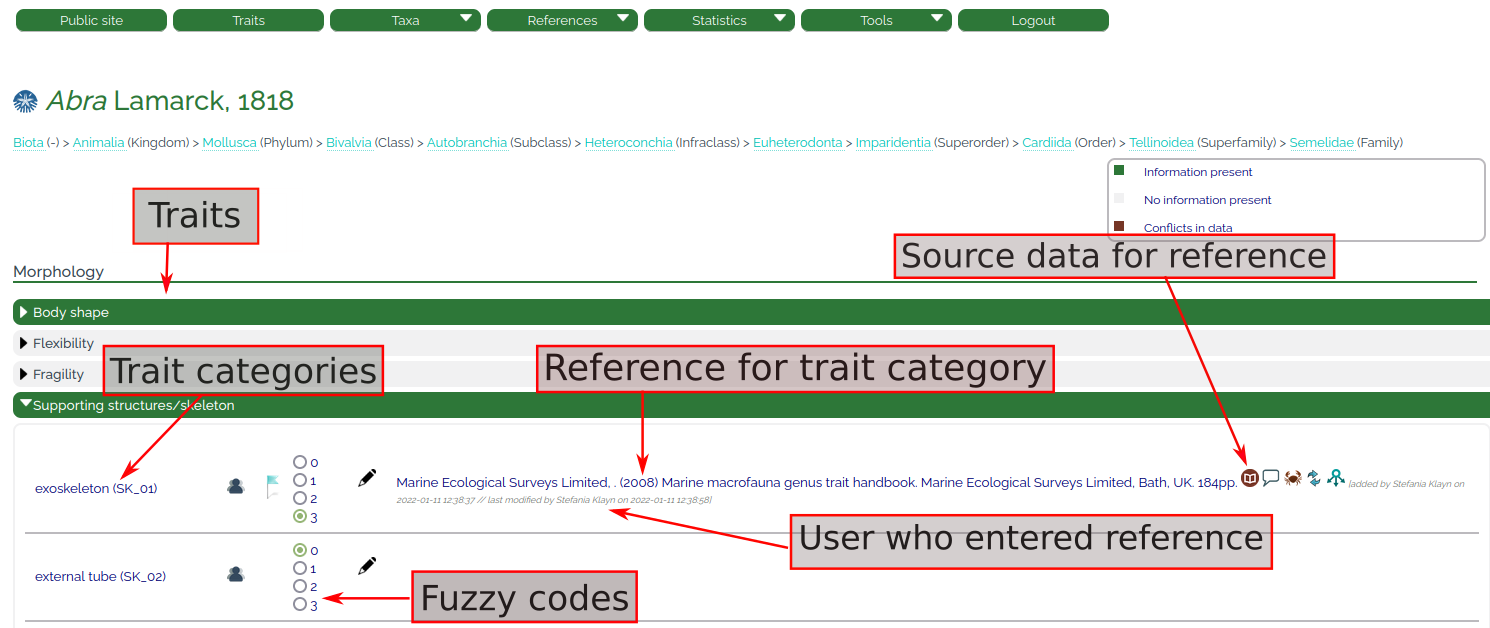
Once a taxon is added to the database, it has its own taxon page (Fig. 5) and trait information to each of the traits and trait categories can be added. Below the taxon (and author) name, the taxonomic tree (derived from WoRMS) is displayed. The WoRMS logo (left of the taxon name) directly links to the WoRMS taxon page of – in this example –Mytilus galloprovincialis. All traits are highlighted in light grey color, indicating that so far, no trait information has been entered for this taxon.
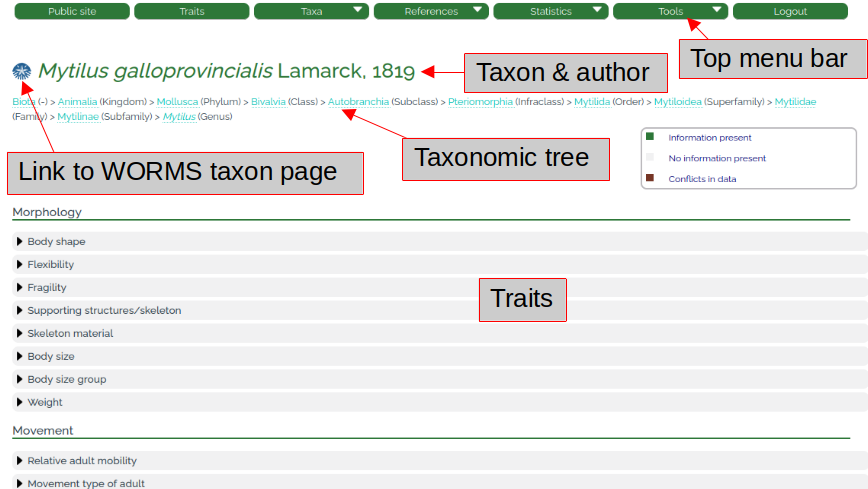
The data in the database are organized in the format of taxon – trait – trait categories – fuzzy codes – references (Fig. 6). When moving the mouse cursor over a trait category (e.g. SK_01 "exoskeleton" in Fig. 6), the trait definition is shown in a small window ("A rigid external structure that supports and/or protects the body of an organism and that is mainly or completely secreted by the epidermis (derived from Lawrence 2005). Includes shells."). For each trait category, a fuzzy value from 0 to 3 can be checked per mouse click and must be supported by at least one reference. This guaranties that no trait information in the entire database is without a source information. In the example below (Fig. 6), a user checked the fuzzy code "3" and added references to the trait category SK_01 ("exoskeleton"). Once information is added, the color of the respective trait changes from light grey to green (after the page is reloaded).
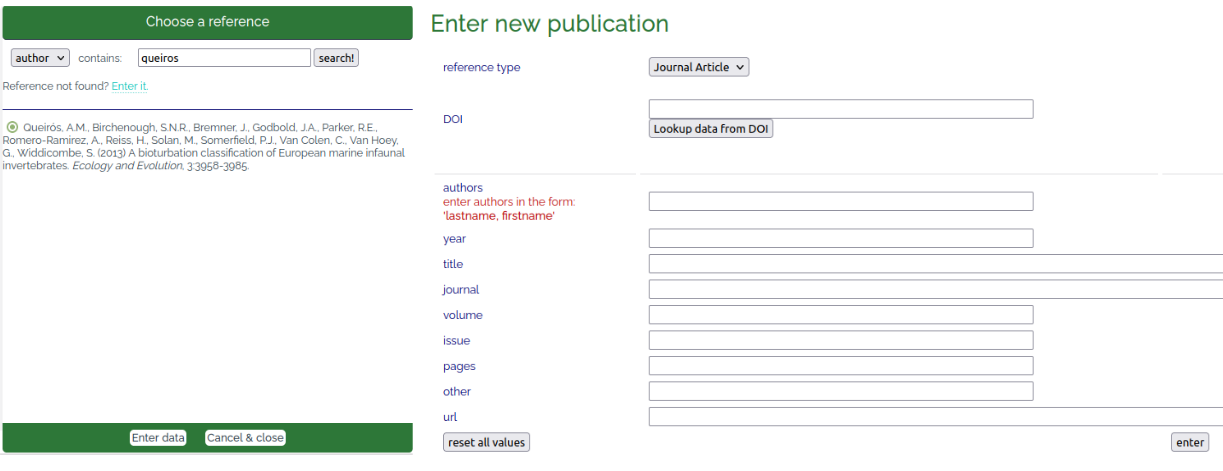
The exact reference needs to be chosen from the database bibliography via a window that opens automatically once a fuzzy code is entered (Fig. 7, left). The search options are "author", "title", "year", "journal", "DOI", "url", and "other". The option "other" is included because trait information does not always stem from published literature, but from communication with experts. In such cases, the name of the taxonomic expert that passed on the information can be entered in the "Enter new publication" window (Fig. 7, right). In such cases the reference type "Other" needs to be selected. Also, the event of a "Personal observation", i.e. when the user personally observed or measured a certain trait, is included in the option "other". The "enter new publication" window is needed in any case when the respective reference (published or communicated) is not yet included in the database bibliography. Then the entire bibliographic information (reference type, authors, year, title, journal, …) needs to be entered. The use of the "Lookup data from DOI" option speeds up the process, as manual entry is no longer required in that case. Additional references can be added at any time via the "References" section in the top menu bar (Fig. 2, Table 1).
Once a reference is selected, the exact source information (raw data, quote of the text that led to the choice of the fuzzy value, table or page number) can be entered in another popup window via the "source" symbol (book icon, Table 6) (Fig. 8). This allows other users to understand which information led to the assignment of the taxon to a specific trait category. It also provides a means for quality control and for reuse of the information in different contexts (Faulwetter et al. 2014). This is especially helpful if a specific research question might require different trait categories than those that have been chosen in the Black Sea Traits Database. In the example in Fig. 8, text information from Queirós et al. (2013), pp. 3961-3982, is entered to support the coding of a trait category.

The "comment" symbol (speech bubble icon, Table 2) allows to add a personal comment to the entered trait information, or to the information entered by other users.
The "taxonomy" symbol (crab icon, Table 2) allows to copy or shift the trait information to another taxon, allowing for rapid entry of characteristics and references that are valid for several taxa. In general, the information is always assigned to the most specific taxon possible.
The "move" symbol (two arrows icon, Table 2) allows to move or copy the entered trait information and reference to another trait category. This is useful when the quote is appropriate for several categories of one trait, to avoid repeating working steps and to save time.
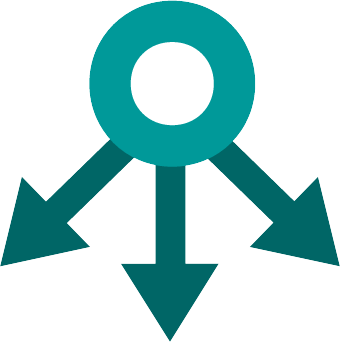
If data is entered for a taxon that has child taxa (i.e. on genus level or higher), also the "child taxa" symbol (down arrow icon, Table 2) is visible. It allows to copy the entered fuzzy code, reference, detailed trait information and comments to all child taxa (e.g. all members of the current family) of the specific taxon. This function has to be used very carefully, as – in case the copied information later proves to be wrong – potentially dozens of wrong entries have to be deleted manually.
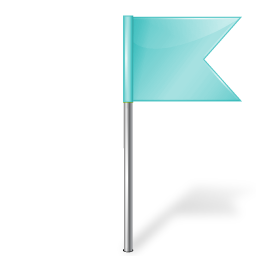
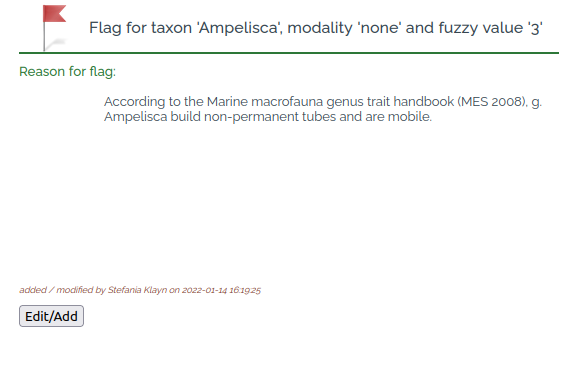
Once a reference is entered, a "blue flag" symbol (Table 2) shows up next to the fuzzy codes (Fig. 6). If users disagree concerning the fuzzy coding or the underlying reference, the color of the flag can be changed to red (Table 2) via mouse click, indicating a "conflict" (Fig. 10). The reason for the disagreement can be entered in a window, thus enabling a discussion among users (Fig. 11). A list of all data with conflicts can be accessed via the "tools" section in the top window (Fig. 2). Conflicts can only be resolved by the editor of the database after sound evaluation of the comments and suggestions by the users. In this event, the flag will then be changed back to blue. Unsolved conflicts will keep the red flag and the respective trait will not be included in the download in order to avoid distributing disputable information.
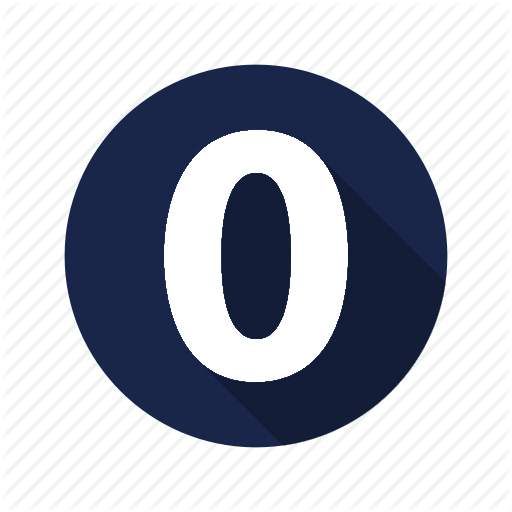
Other conflicts may appear due to data entry errors. Cases where a reference is present but all fuzzy codes are "0" will be marked by the "zero" symbol (Table 2). Cases where the entered fuzzy codes are conflicting (e.g. “3” is entered twice for one trait, or a “2” and a “3” are entered) will be marked by the “crash” symbol (meeting arrows icon, Table 2). Such conflicts can be filtered for from the total dataset in the “Tools” section and resolved by the editor or registered users.
| Symbol | Action / Interpretation |
|---|---|
 |
Source – original quote from reference, page number |
 |
Comment – e.g. to explain your choice of coding (not mandatory). |
 |
Taxonomy – Move or copy trait information to other taxa. |
 |
Move or copy trait information to another trait or trait category. |
 |
Copy trait information to all child taxa. |
 |
Trait information is present and there are no conflicts |
 |
Conflict – disagreement among users. |
 |
Conflict – All fuzzy codes are set to “0”. |
 |
Conflict – Fuzzy codes are conflicting (e.g. codes “2” and “3” in one category) |
Once trait information and references have been entered, the appearance of the respective taxon page changes (Fig. 9). Registered users will see that traits where no information is currently present are highlighted in light grey, traits with information are highlighted in green, and traits where any of the conflicts mentioned above exist are now highlighted in brown. Once a conflict is resolved, the color will change from brown to green after the page is reloaded. The taxon page visible via the public access shows only those traits that have complete information in green, while absent traits are highlighted in light grey and conflicts are not visible at all.
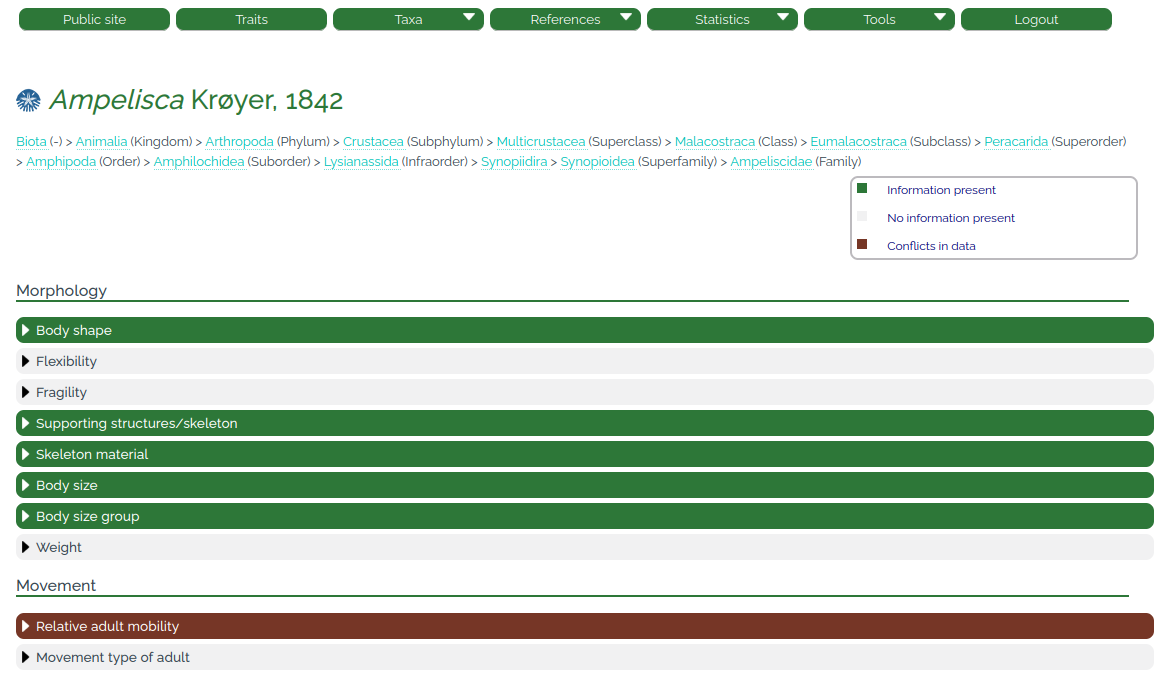

6. References
- Faulwetter, S., Markantonatou, V., Pavloudi, C., Papageorgiou, N., Keklikoglou, K., Chatzinikolaou, E., Pafilis, E., Chatzigeorgiou, G., Vasileiadou, K., Dailianis, T., Fanini, L., Koulouri, P., Arvanitidis, C., 2014. Polytraits: A database on biological traits of marine polychaetes. Biodivers. Data J. 2, e1024. doi:10.3897/BDJ.2.e1024
- Queirós, A.M., Birchenough, S.N.R., Bremner, J., Godbold, J.A., Parker, R.E., Romero-Ramirez, A., Reiss, H., Solan, M., Somerfield, P.J., Van Colen, C., Van Hoey, G., Widdicombe, S., 2013. A bioturbation classification of European marine infaunal invertebrates. Ecol. Evol. 3, 3958–3985. doi:10.1002/ece3.769
- WoRMS Editorial Board, 2021. World Register of Marine Species. Available from http://www.marinespecies.org at VLIZ. Accessed 2021-08-16. doi:10.14284/170.


